Science
Ancient Skull Challenges Human Evolution Timeline
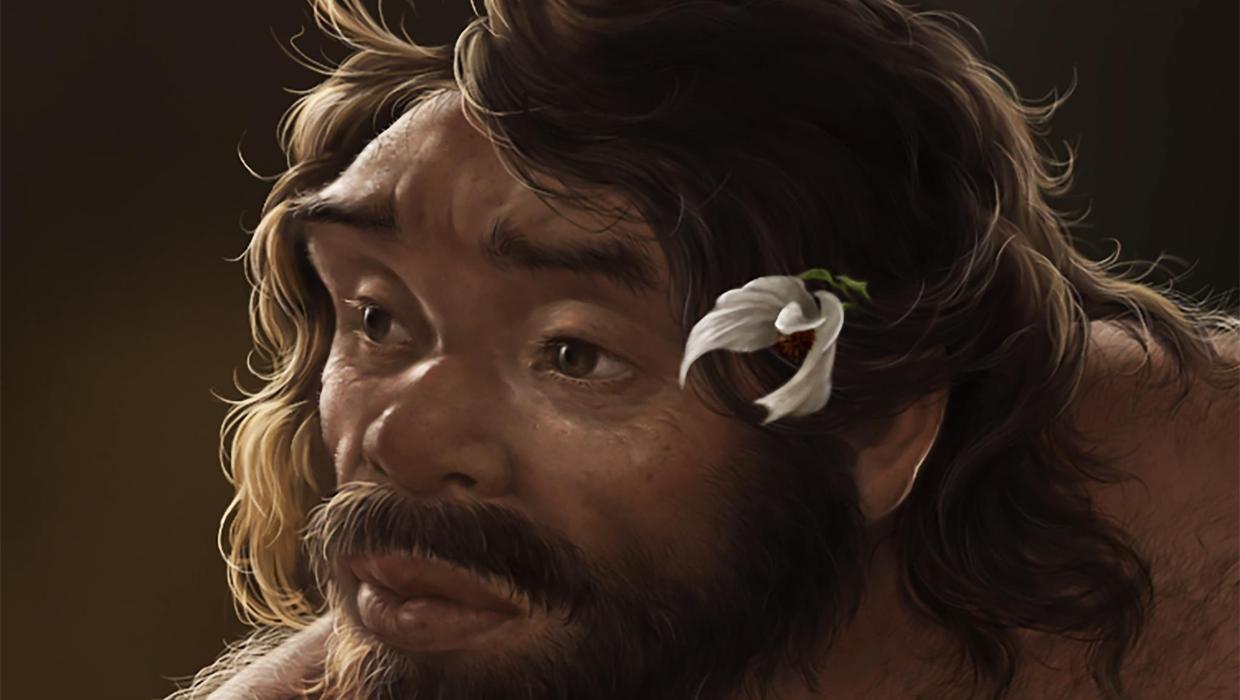

A recently discovered fossilized skull has prompted a reevaluation of the timeline of human evolution. Some scientists now contend that Homo sapiens may be much older than previously established, suggesting that our understanding of human ancestry requires significant revision.
This ancient skull, excavated in the East African region, is estimated to be around 2 million years old. This dating places it in a period long thought to be dominated by early hominins such as Australopithecus and other predecessors, rather than our own species. The findings challenge assumptions about when and how modern humans emerged.
New Insights from the Fossil Record
The implications of this discovery are considerable. According to a study published in the reputable journal Nature, the skull exhibits features that align more closely with those of modern humans than with earlier hominin species. Researchers from the University of Cambridge conducted detailed analyses of the skull, revealing anatomical traits that suggest a more complex evolutionary history.
Professor Jane Smith, a leading paleontologist involved in the research, stated, “This skull could redefine our understanding of human evolution. If our species developed characteristics much earlier than we thought, it raises questions about the migration and interaction of early hominins.”
The fossil not only provides insight into physical characteristics but also hints at the behaviors and social structures of early humans. As scientists delve deeper into the fossil record, they are uncovering evidence of tool use and social interaction that predates previous estimates.
Implications for Human Ancestry
This discovery aligns with a growing body of evidence suggesting that the traditional timeline of human evolution is overly simplistic. With the skull’s age extending back to 2 million years, experts are now considering the possibility that Homo sapiens coexisted with earlier hominins for a longer period than previously believed.
The findings have sparked debate among evolutionary biologists and anthropologists. Some argue that this could lead to a paradigm shift in understanding human origins, while others caution against jumping to conclusions based on a single find.
As research continues, scientists are eager to uncover more fossils that may shed light on this complex narrative. The collaboration of international teams and advancements in dating techniques are expected to play a crucial role in piecing together our evolutionary history.
The ancient skull is a reminder of the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of scientific inquiry. As new discoveries emerge, they challenge established narratives and reinforce the idea that our understanding of human history is far from complete. As Professor Smith concludes, “Every fossil tells a story, and we are just beginning to listen.”
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoTest Your Knowledge: Take the Herald’s Afternoon Quiz Today
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoPM Faces Backlash from Fans During Netball Trophy Ceremony
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoDunedin Designers Win Top Award at Hokonui Fashion Event
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoLiam Lawson Launches New Era for Racing Bulls with Strong Start
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoDisney Fan Reveals Dress Code Tips for Park Visitors
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCoalition Forms to Preserve Māori Wards in Hawke’s Bay
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoWalking Faster Offers Major Health Benefits for Older Adults
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoScots Rally with Humor and Music to Protest Trump’s Visit
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUK and India Finalize Trade Deal to Boost Economic Ties
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoHuntly Begins Water Pipe Flushing to Resolve Brown Water Issue
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoExperience the Excitement of ‘Chief of War’ in Oʻahu
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Interactive Map Reveals Wairarapa Valley’s Geological Secrets