Science
Fossil Skull Challenges Human Evolution Timeline, Sparks Debate
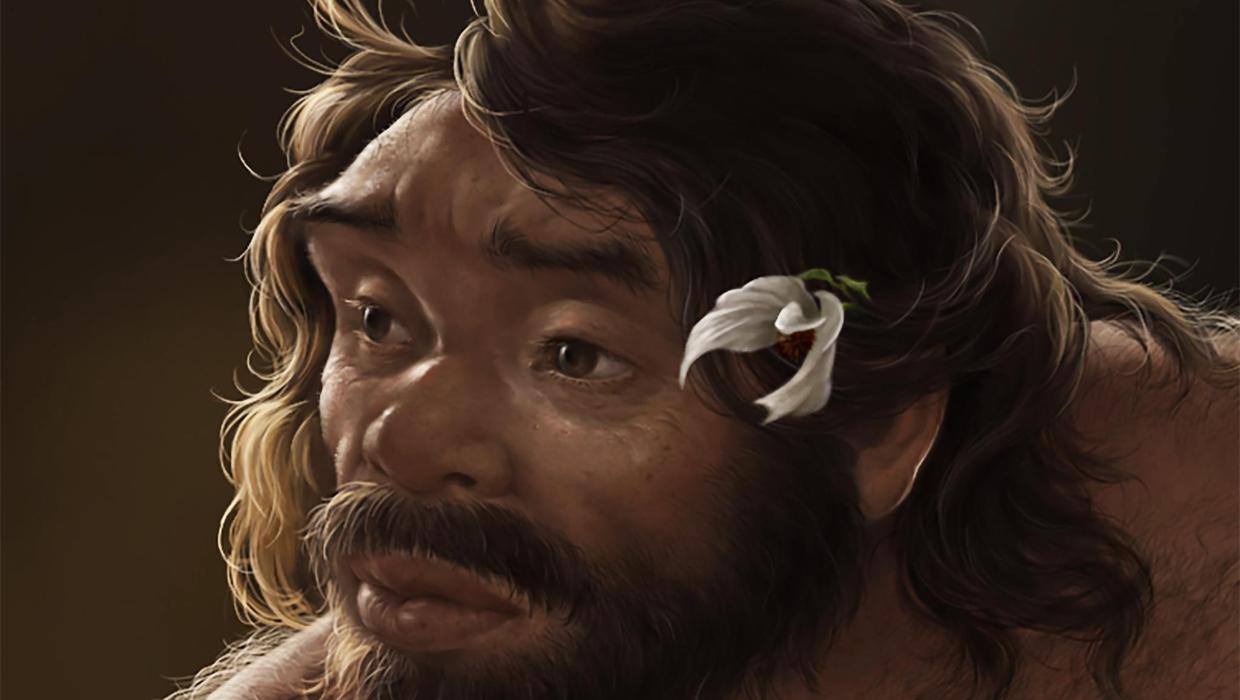

A recently discovered fossilised skull is prompting a reevaluation of the timeline of human evolution. This finding suggests that the origins of our species may be significantly older than previously established, sparking a lively debate among scientists.
The skull, attributed to the species Homo naledi, was uncovered in a cave system in South Africa. Researchers from the University of the Witwatersrand have dated the skull to be around 300,000 years old. This contradicts earlier beliefs that modern humans, or Homo sapiens, emerged approximately 200,000 years ago.
Dr. Lee Berger, the lead researcher and palaeoanthropologist at the University of the Witwatersrand, stated, “This finding indicates that our understanding of human evolution is far more complex than we previously thought.” The skull exhibits a mix of primitive and modern features, which further complicates the evolutionary picture.
The implications of this discovery are profound. If Homo naledi existed concurrently with early humans, it raises questions about potential interactions between different hominin species. Such interactions could have influenced the development of early human behaviour, culture, and even technology.
The research team published their findings in the journal Nature, where they presented evidence that Homo naledi may have engaged in practices such as burial and symbolic behaviour, traits traditionally associated with modern humans. This challenges the established views of cognitive abilities and social structures among early hominins.
Dr. Berger’s team conducted extensive analyses on the skull, utilizing advanced imaging techniques to study its morphology. They also examined artifacts found in the same region, further supporting their claims about the complexity of early human life.
The discovery has drawn attention from scientists worldwide. According to a report by National Geographic, this skull could rewrite the narrative of human evolution, highlighting the need for further research into the relationships between different hominin species.
As debates continue, many researchers emphasize the importance of integrating new findings into existing evolutionary models. “Understanding our past is crucial for comprehending our future,” Dr. Berger noted, urging the scientific community to remain open to new evidence as it emerges.
In summary, the fossilised skull of Homo naledi not only challenges the established timeline of human evolution but also invites a deeper investigation into the interactions and adaptations of our ancient relatives. As more discoveries are made, the story of human evolution continues to evolve, much like the species it aims to explain.
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoTest Your Knowledge: Take the Herald’s Afternoon Quiz Today
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoPM Faces Backlash from Fans During Netball Trophy Ceremony
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoDunedin Designers Win Top Award at Hokonui Fashion Event
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoLiam Lawson Launches New Era for Racing Bulls with Strong Start
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoDisney Fan Reveals Dress Code Tips for Park Visitors
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoWalking Faster Offers Major Health Benefits for Older Adults
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCoalition Forms to Preserve Māori Wards in Hawke’s Bay
-

 Politics3 months ago
Politics3 months agoScots Rally with Humor and Music to Protest Trump’s Visit
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUK and India Finalize Trade Deal to Boost Economic Ties
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoHuntly Begins Water Pipe Flushing to Resolve Brown Water Issue
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoExperience the Excitement of ‘Chief of War’ in Oʻahu
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoNew Interactive Map Reveals Wairarapa Valley’s Geological Secrets